Create a Civo Kubernetes cluster
Every new Civo account receives $250 in credit to get started with the GitLab integration with Civo Kubernetes. You can also use a marketplace app to install GitLab on your Civo Kubernetes cluster.
Learn how to create a new cluster on Civo Kubernetes through Infrastructure as Code (IaC). This process uses the Civo and Kubernetes Terraform providers to create Civo Kubernetes clusters. You connect the clusters to GitLab by using the GitLab agent for Kubernetes.
Before you begin:
- A Civo account.
- A runner you can use to run the GitLab CI/CD pipeline.
Steps:
- Import the example project.
- Register the agent for Kubernetes.
- Configure your project.
- Provision your cluster.
Import the example project
To create a cluster from GitLab using Infrastructure as Code, you must create a project to manage the cluster from. In this tutorial, you start with a sample project and modify it according to your needs.
Start by importing the example project by URL.
To import the project:
- In GitLab, on the left sidebar, select Search or go to.
- Select View all my projects..
- On the right of the page, select New project.
- Select Import project.
- Select Repository by URL.
- For the Git repository URL, enter
https://gitlab.com/civocloud/gitlab-terraform-civo.git. - Complete the fields and select Create project.
This project provides you with:
- A cluster on Civo with defaults for name, region, node count, and Kubernetes version.
- The GitLab agent for Kubernetes installed in the cluster.
Register the agent
To create a GitLab agent for Kubernetes:
- On the left sidebar, select Operate > Kubernetes clusters.
- Select Connect a cluster.
- From the Select an agent dropdown list, select
civo-agentand select Register. - GitLab generates an agent access token for the agent. Securely store this secret token, as you will need it later.
- GitLab provides an address for the agent server (KAS), which you will also need later.
Configure your project
Use CI/CD environment variables to configure your project.
Required configuration:
- On the left sidebar, select Settings > CI/CD.
- Expand Variables.
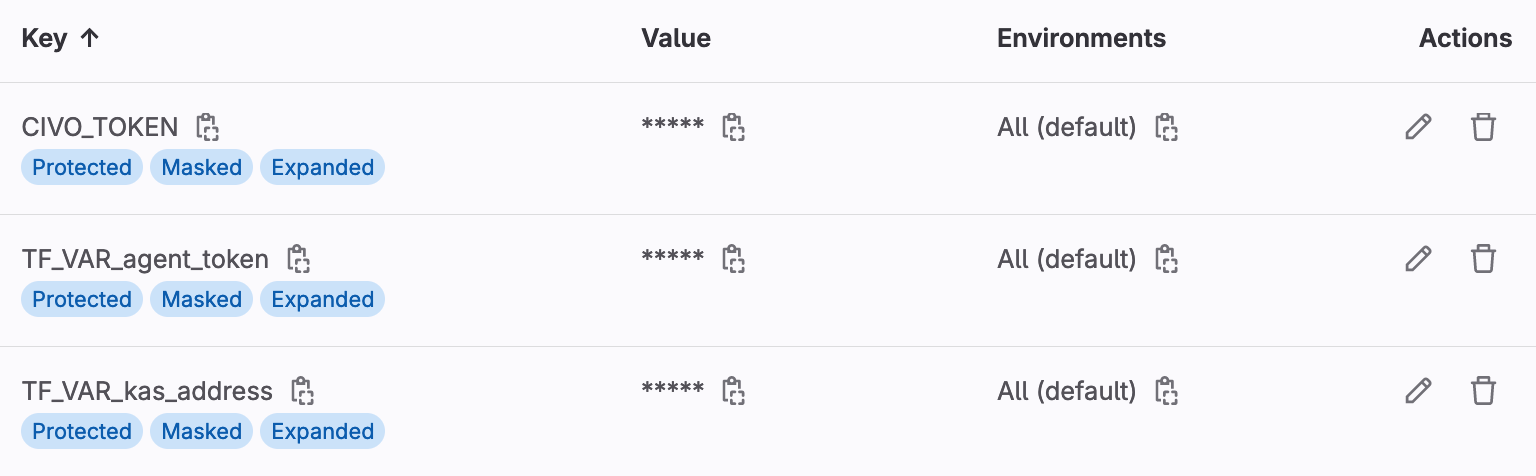
- Set the variable
CIVO_TOKENto the token from your Civo account. - Set the variable
TF_VAR_agent_tokento the agent token you received in the previous task. - Set the variable
TF_VAR_kas_addressto the agent server address in the previous task.
Optional configuration:
The file variables.tf
contains other variables that you can override according to your needs:
-
TF_VAR_civo_region: Set your cluster's region. -
TF_VAR_cluster_name: Set your cluster's name. -
TF_VAR_cluster_description: Set a description for the cluster. To create a reference to your GitLab project on your Civo cluster detail page, set this value to$CI_PROJECT_URL. This value helps you determine which project was responsible for provisioning the cluster you see on the Civo dashboard. -
TF_VAR_target_nodes_size: Set the size of the nodes to use for the cluster -
TF_VAR_num_target_nodes: Set the number of Kubernetes nodes. -
TF_VAR_agent_version: Set the version of the GitLab agent. -
TF_VAR_agent_namespace: Set the Kubernetes namespace for the GitLab agent.
Refer to the Civo Terraform provider and the Kubernetes Terraform provider documentation for further resource options.
Provision your cluster
After configuring your project, manually trigger the provisioning of your cluster. In GitLab:
- On the left sidebar, select Build > Pipelines.
- Select New pipeline.
- Select Run pipeline, and then select the newly created pipeline from the list.
- Next to the deploy job, select Manual action ({status_manual}).
When the pipeline finishes successfully, you can see your new cluster:
- In Civo dashboard: on your Kubernetes tab.
- In GitLab: from your project's sidebar, select Operate > Kubernetes clusters.
If you didn't set the TF_VAR_civo_region variable, the cluster will be created in the 'lon1' region.
Use your cluster
After you provision the cluster, it is connected to GitLab and is ready for deployments. To check the connection:
- On the left sidebar, select Operate > Kubernetes clusters.
- In the list, view the Connection status column.
For more information about the capabilities of the connection, see the GitLab agent for Kubernetes documentation.
Remove the cluster
A cleanup job is included in your pipeline by default.
To remove all created resources:
- On the left sidebar, select Build > Pipelines, and then select the most recent pipeline.
- Next to the destroy-environment job, select Manual action ({status_manual}).
Civo support
This Civo integration is supported by Civo. Send your support requests to Civo support.